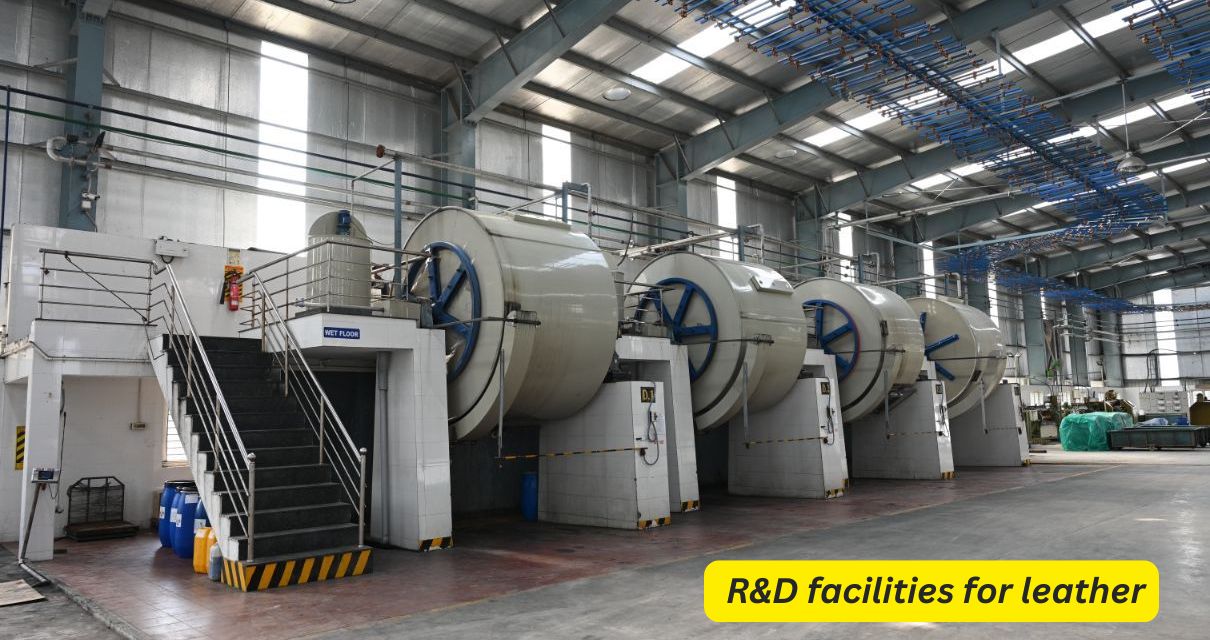
As of now, there are no specific references to dedicated Research and Development (R&D) facilities solely based in Panapakkam. However, R&D for leather innovation in the region is supported through a combination of industry collaborations, government initiatives, and partnerships with research institutions.
Here are some key points regarding R&D activities and innovation related to Panapakkam’s leather industry:
1. Leather Sector Skill Council (LSSC)
- While primarily focused on skill development, the LSSC also plays a role in facilitating technological advancements in the leather industry. Through partnerships with educational institutions and industry bodies, LSSC helps promote the adoption of new manufacturing techniques, sustainable practices, and innovations in leather production.
2. Tamil Nadu’s Focus on Leather Innovation
- The Tamil Nadu government has made significant strides in supporting leather innovation through its various policies, including the Tamil Nadu Footwear and Leather Products Policy 2022. While the policy focuses more on promoting production, it also highlights the importance of technology adoption and research to stay competitive in the global market.
3. National and International Collaborations
- Central Leather Research Institute (CLRI), Chennai: Although not based in Panapakkam, the CLRI, located in Chennai (about 100 km away), is India’s premier institution for leather research. CLRI conducts extensive research on leather processing, tanning technologies, and sustainable leather production. The institute collaborates with industries across India, including Panapakkam’s leather manufacturers, to bring innovations and environmentally friendly solutions to the market.
4. Industry-Specific Innovations
- Many leather manufacturing units in Panapakkam are likely to adopt innovations in eco-friendly tanning methods, waste reduction, leather recycling, and biodegradable materials as global demand for sustainable products grows. Innovations in smart factories and automation are also transforming how leather is produced and processed.
5. Private and Industry-Led R&D Initiatives
- Some major leather manufacturers in the region may have their own R&D departments, focusing on improving product quality, reducing production costs, and enhancing leather’s environmental footprint. For example, there is an increasing trend of using vegetable tanning, chrome-free tanning methods, and alternative raw materials in response to the demand for more sustainable leather goods.
6. Support from Global Standards and Certifications
- Manufacturers in Panapakkam may also engage in research to meet international standards like the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which drives innovation toward more sustainable leather production practices. By focusing on eco-friendly practices, these manufacturers contribute to technological advancements in leather processing.
While Panapakkam itself may not have large-scale dedicated R&D facilities for leather innovation, there are considerable efforts at the state and national levels to encourage research, sustainable development, and technological advancements. Leather manufacturers in Panapakkam likely benefit from these initiatives and collaborate with nearby institutions such as CLRI in Chennai to adopt innovations and maintain competitiveness in the global leather market.