The process of cutting and stitching leather for garment production involves precise techniques to ensure quality, durability, and aesthetics. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
1. Leather Selection and Preparation
- Step: High-quality hides or skins are selected based on thickness, flexibility, and smoothness.
- Preparation:
- Leather is softened using conditioning methods.
- Imperfections like scars are identified to minimize waste during cutting.
2. Pattern Making
- Step: Patterns for garments (jackets, trousers, coats) are created using paper or digital software (CAD systems).
- Key Consideration: Patterns are laid to optimize leather use and avoid damaged areas.
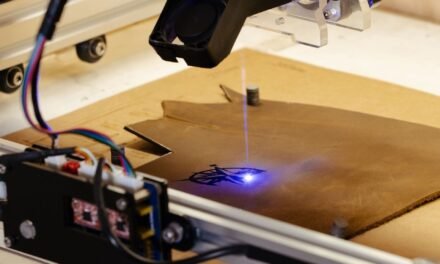
3. Leather Cutting
- Manual Cutting:
- Skilled workers use sharp knives or scalpels for precise cuts, ensuring accuracy along the pattern edges.
- This method is used for small-scale or custom production.
- Machine Cutting:
- For large-scale production, die-cutting machines or laser cutters ensure speed and uniformity.
- Challenges: Leather has no stretch (unlike fabric), so precision is critical to avoid errors.
4. Skiving (Edge Thinning)
- Step: Edges of leather pieces are thinned down to reduce bulk at seams and enhance flexibility.
- Tools Used:
- Skiving machines or manual tools like blades.
5. Stitching Leather Pieces
- Step: Leather pieces are stitched together using heavy-duty sewing machines designed for thick materials.
- Techniques Used:
- Lock Stitch: Common for durable seams.
- Top Stitching: Decorative and functional stitching along seams for reinforcement.
- Thread:
- Nylon, polyester, or waxed threads are used for strength.
- Thicker threads ensure the seams withstand stress.
- Needles: Special leather needles with wedge-shaped tips prevent tearing.
6. Seam Finishing
- Step: Seams are pressed flat and sometimes reinforced with leather glues or topstitching for durability.
- Optional: Edges may be treated with finishes (e.g., burnishing or edge paint) for a smooth, polished look.
7. Final Assembly and Detailing
- Step: Additional details like zippers, buttons, linings, and trims are added.
- Attention to Detail:
- Precise alignment of seams and components ensures a professional finish.
8. Quality Control
- Step: The finished garment undergoes inspection for:
- Stitch strength and alignment.
- Smooth seams and polished edges.
- Proper fitting and finishing.