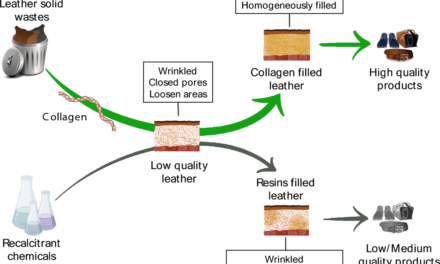
Recycling and upcycling play a crucial role in the leather industry’s sustainability efforts by reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting a circular economy. These practices address environmental concerns while adding economic and creative value to leather production.
Key Roles of Recycling and Upcycling in Leather Sustainability
- Minimizing Waste
- Leather production generates significant off-cuts, scraps, and trimmings. Recycling processes repurpose these materials into bonded leather or composite products, preventing them from ending up in landfills.
- Creating Recycled Leather
- Scraps are shredded and reconstituted using natural or synthetic binders to produce recycled leather. This is used for upholstery, footwear, and accessories, reducing the need for fresh raw materials.
- Promoting Upcycling for High-Value Products
- Upcycling transforms discarded leather and old products into new, unique, and high-value goods, such as bags, wallets, footwear, and home décor.
- Example: Old leather jackets are turned into stylish handbags, extending product lifespans and reducing environmental impact.
- Reducing Resource Consumption
- Recycling leather requires fewer resources (like water and energy) compared to producing new leather, thereby lowering the carbon footprint of the industry.
- Supporting a Circular Economy
- By reusing materials, the leather industry aligns with circular economy principles, ensuring materials stay in use for as long as possible.
- Addressing Environmental Impact
- Recycling reduces landfill pressure and the need for fresh raw hides, which lowers environmental stress caused by livestock farming.
- Upcycling creatively combats the issue of overproduction and fast fashion waste.
- Innovation and Creativity
- Advances in recycling technologies allow brands to create durable and sustainable leather alternatives, while upcycling fosters innovation through custom, artisanal products.
- Consumer Demand for Sustainability
- Eco-conscious consumers are driving brands to adopt recycling and upcycling processes, furthering transparency and accountability in the supply chain.