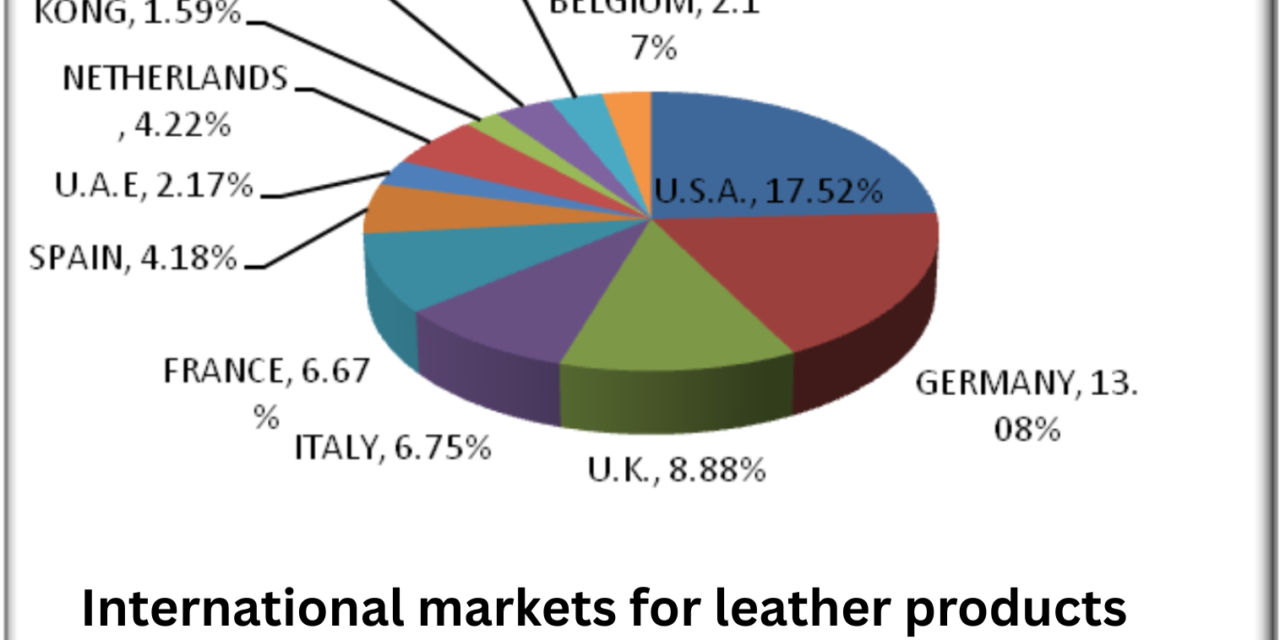
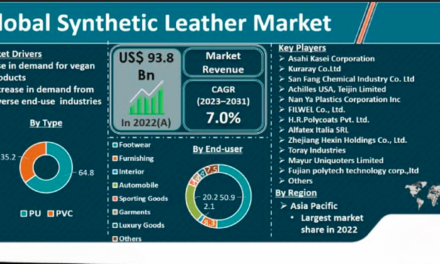
Governments play a key role in promoting leather products in international markets through various policies, programs, and initiatives designed to enhance the competitiveness of the leather industry. Here are several ways in which governments support and promote leather products globally:
1. Export Incentives and Financial Support:
- Export Promotion Schemes: Many governments offer export incentives to encourage the international trade of leather products. This can include duty drawbacks, tax exemptions, and subsidies for companies exporting leather goods. For example, in countries like India, the government offers schemes under the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) to incentivize exporters of leather goods and footwear.
2. Trade Agreements and Bilateral Partnerships:
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs): Governments negotiate trade agreements to reduce tariffs and trade barriers for leather products. FTAs allow leather products to enter foreign markets at lower customs duties, making them more competitive. For example, India’s FTAs with the European Union, the United States, and other countries have facilitated smoother exports of leather goods.
3. Support for Industry Standards and Certifications:
- Quality Standards and Certifications: Governments may help leather manufacturers meet international quality standards by facilitating access to certifications such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization), Sustainable Practices Promotion: As demand for environmentally friendly products grows, governments promote sustainability initiatives and ensure that leather products meet international environmental standards. This can improve the global competitiveness of the industry.
4. Market Access and Promotion Activities:
- Trade Fairs and Exhibitions: Governments often sponsor participation in international trade fairs, exhibitions, and conferences dedicated to leather goods. For example, many countries support their leather industry by funding participation in global events like the Lineapelle Leather Fair in Milan or the India International Leather Fair. These platforms allow manufacturers to showcase their products, meet potential buyers, and build networks.
- Trade Missions: Governments organize trade missions to foreign countries, where leather manufacturers can meet with international buyers, distributors, and retailers. These missions are designed to explore new markets and increase the export potential of leather products.
5. Training and Capacity Building:
- Skill Development Programs: To improve the quality of leather products and increase their competitiveness in international markets, governments invest in skill development and training programs for workers in the leather sector. These programs focus on upgrading technical skills in design, manufacturing, and finishing techniques to meet global demand.
- Research and Development: Governments may fund research and development (R&D) activities aimed at improving the production processes, quality, and innovation in the leather industry. This ensures that manufacturers can offer products that meet changing global market trends and standards.
6. Creating Export-Ready Infrastructure:
- Industrial Parks and Clusters: Governments create specialized industrial zones and clusters, like the Leather Export Zones (LEZs) or Leather Parks, where leather businesses can access world-class infrastructure, including transport, logistics, and utility services, to facilitate export operations.
- Logistics and Shipping Support: By investing in efficient transportation infrastructure, such as ports, airports, and logistics hubs, governments help reduce costs and improve the speed of exporting leather products. This includes facilitating direct shipping routes to key markets.
7. Brand Building and National Image:
- Country Branding: Governments often work on branding their country’s leather products to enhance their global image. For example, Italy has successfully built a reputation for high-quality leather goods, and the Indian government’s initiatives help position the country as a significant exporter of leather and footwear.
- Digital Promotion: Governments and trade associations also leverage digital marketing platforms to promote their country’s leather products, using e-commerce platforms, social media, and online campaigns to reach international buyers.
8. Collaborations with Trade Associations:
- Public-Private Partnerships: Governments often collaborate with trade associations and industry bodies, such as the Council for Leather Exports (CLE) in India or the National Leather Association (NLA), to develop programs that enhance the international competitiveness of leather products. These collaborations focus on market research, export strategies, and policy advocacy to improve trade opportunities.
9. Support for Innovation and Product Diversification:
- Innovation Hubs: Governments may set up innovation hubs where companies can experiment with new leather products, such as eco-friendly and cruelty-free alternatives, and adopt cutting-edge technologies in design and production.
- Diversification of Leather Products: Governments encourage leather producers to diversify their product offerings to cater to various international markets, such as footwear, automotive leather, furniture, fashion accessories, and industrial leather goods. This diversification helps mitigate risks and opens up new export opportunities.