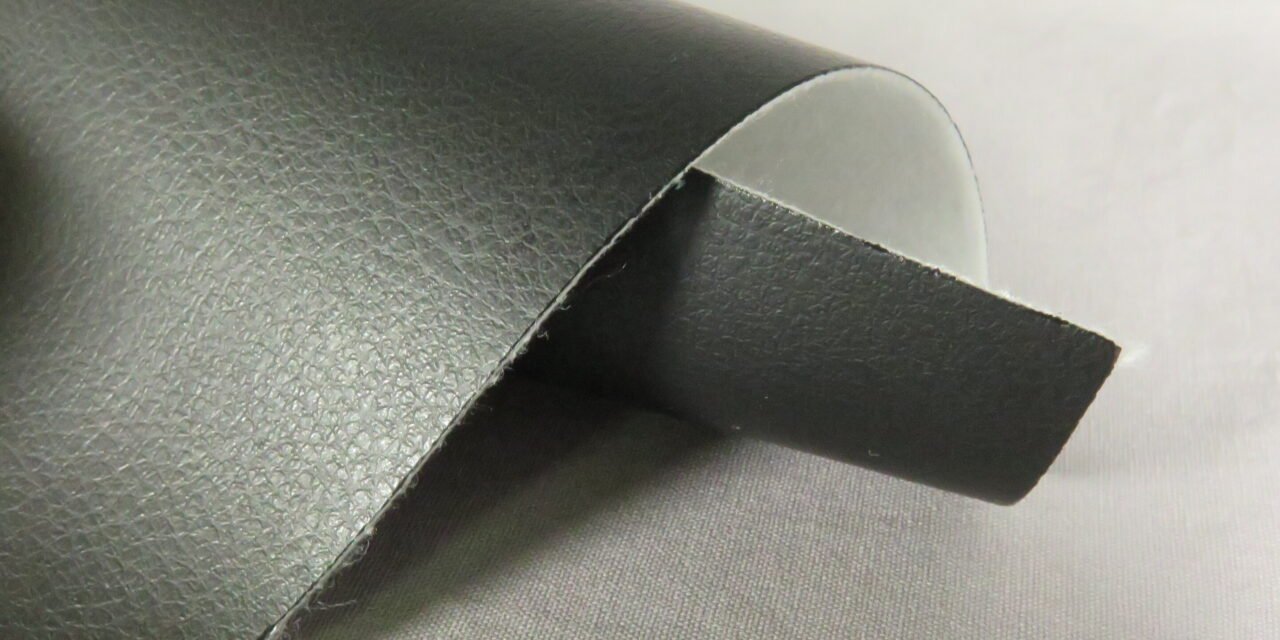
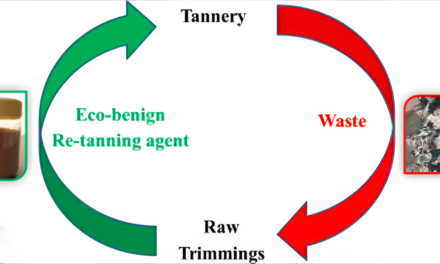
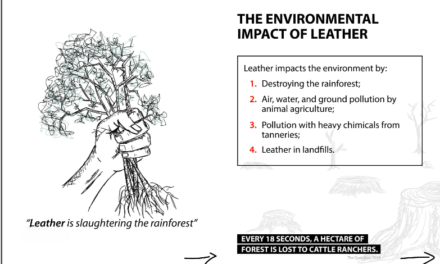
Recycling synthetic leather is challenging due to its composite structure, which combines plastic polymers (such as polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride) with fabric backings. However, advancements in technology and sustainability initiatives are making synthetic leather recycling more feasible. Here’s an overview of how synthetic leather can be recycled:
1. Mechanical Recycling
This method involves shredding and processing synthetic leather into smaller pieces for reuse.
Steps:
- Collection:
- Gather synthetic leather waste from manufacturing offcuts, discarded products, or post-consumer items.
- Shredding:
- The material is shredded into smaller particles or fibers.
- Reprocessing:
- The shredded material is blended with virgin or recycled plastics to create new composite materials.
- Applications:
- Used to produce items like floor mats, padding, insulation, or lower-grade synthetic leather products.
Challenges:
- The adhesive bond between the plastic and fabric layers makes separation difficult, reducing material quality.
- Recycling often downgrades the material, limiting its applications.
2. Chemical Recycling
This process uses chemical treatments to break down synthetic leather into its base components for reuse.
Steps:
- Material Separation:
- Chemicals dissolve the plastic layers (e.g., PU or PVC) and separate them from the fabric backing.
- Component Recovery:
- The dissolved plastic is purified and processed into pellets or sheets for reuse.
- The fabric may be recycled into fibers or textiles.
- Applications:
- Recovered plastics can be used to produce new synthetic leather or other plastic products.
Challenges:
- High energy and chemical input.
- Potential environmental risks from improper handling of solvents and byproducts.
3. Thermal Recycling (Energy Recovery)
This involves incinerating synthetic leather waste to generate energy.
Steps:
- Collection:
- Synthetic leather waste is gathered for incineration.
- Energy Generation:
- The material is burned in a controlled environment, and the energy released is used to produce electricity or heat.
- Applications:
- Energy recovery reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges:
- Emits greenhouse gases and toxic byproducts if not properly controlled.
- Not a circular recycling method, as it does not repurpose the material into new products.
4. Upcycling
Upcycling transforms synthetic leather waste into new products without breaking it down into raw materials.
Steps:
- Material Collection:
- Collect scraps or used synthetic leather.
- Creative Repurposing:
- Use the material to create smaller accessories like wallets, keychains, or patchwork furniture.
- Applications:
- Ideal for fashion, DIY projects, or small-scale production.
Challenges:
- Limited scalability for industrial applications.
- Requires skilled craftsmanship.
5. Emerging Technologies
Innovations are being developed to improve synthetic leather recycling:
Bio-Based Solutions:
- Bio-based synthetic leathers are easier to recycle as they use biodegradable or renewable polymers.
Advanced Material Separation:
- Technologies like ultrasonic waves, enzymes, or specialized solvents are being tested to efficiently separate plastic layers from fabric backings.
Closed-Loop Recycling:
- Manufacturers are exploring systems where synthetic leather waste is collected and fully recycled into new products without material loss.
6. Recycling by Manufacturers
Some companies are adopting proprietary recycling methods:
Take-Back Programs:
- Brands collect worn-out products and recycle them using their facilities.
In-House Recycling:
- Manufacturing waste (e.g., offcuts) is directly recycled into new batches of synthetic leather.
Applications of Recycled Synthetic Leather
- Lower-Grade Synthetic Leather:
- Used for budget-friendly furniture or accessories.
- Industrial Applications:
- Insulation materials, construction padding, or automotive interiors.
- Eco-Friendly Products:
- Promoted as a sustainable alternative for environmentally conscious consumers.
Challenges in Recycling Synthetic Leather
- Material Complexity:
- Bonded layers of plastic and fabric make separation difficult.
- Energy and Cost:
- Recycling processes can be energy-intensive and expensive compared to producing new materials.
- Quality Degradation:
- Recycled synthetic leather may not match the original quality, limiting its reuse.
- Market Demand:
- Limited demand for recycled synthetic leather products due to competition from cheaper virgin materials.
Conclusion
While recycling synthetic leather is complex, methods like mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and upcycling offer viable solutions to reduce waste. Innovations in material separation and bio-based alternatives are paving the way for more sustainable synthetic leather production and recycling practices. However, widespread adoption will require advancements in technology, cost reductions, and increased consumer awareness.
Hashtags
#RecyclingSyntheticLeather #SustainableFauxLeather #EcoFriendlyLeatherRecycling #SyntheticMaterialReuse #CircularEconomyInLeather #VeganLeatherSustainability #RecycledLeatherAlternatives #SustainableFashionMaterials #FauxLeatherRecycling #SyntheticLeatherWasteManagement