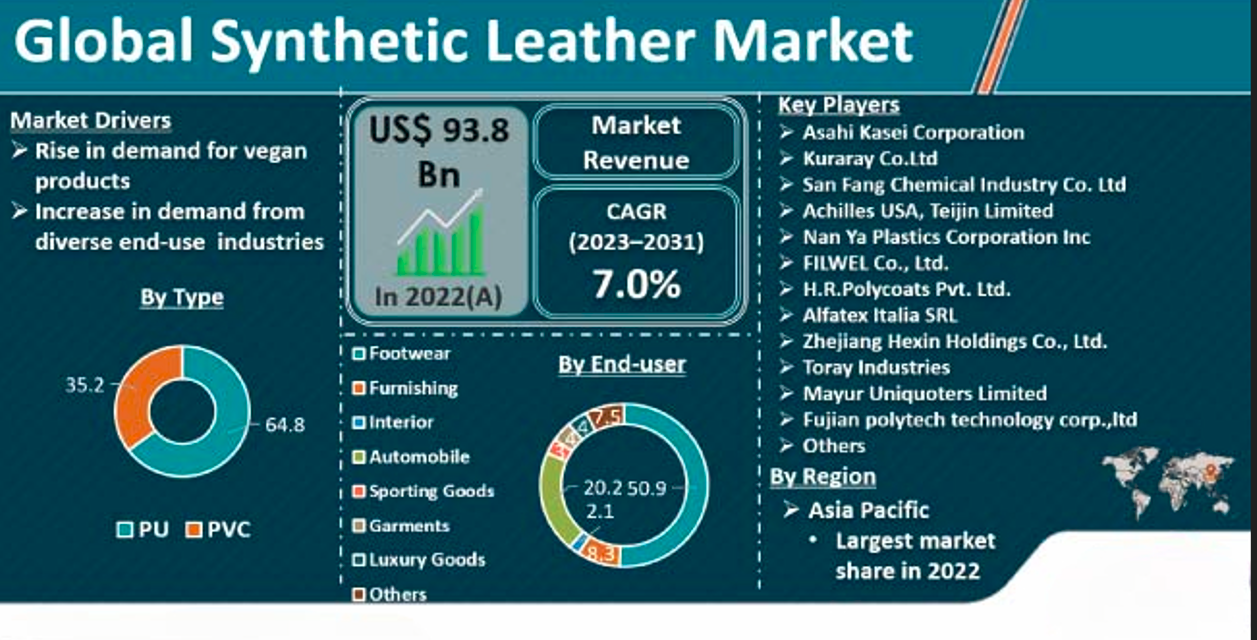
Manufacturing synthetic leather products involves several challenges due to the materials, processes, and market demands. These challenges can affect quality, production efficiency, environmental impact, and market acceptance. Below are the key challenges faced in the production of synthetic leather products:
1. Environmental Concerns
- Non-Biodegradability:
- Traditional synthetic leathers, such as those made from PVC and PU, are derived from petrochemicals and are not biodegradable, leading to long-term environmental pollution.
- Toxic Byproducts:
- PVC manufacturing releases harmful substances like dioxins, which are toxic and pose environmental and health risks.
- Waste Management:
- Managing production waste, including excess polymers and chemical runoff, is challenging and costly.
- Carbon Footprint:
- The production process relies on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Quality Control
- Consistency in Appearance:
- Achieving uniform texture, color, and finish across batches is difficult, especially for large-scale production.
- Material Defects:
- Issues such as uneven coating, bubbles, or cracks during the production process can lead to product rejection.
- Durability:
- Synthetic leather is prone to peeling, cracking, or delamination over time, which can affect product longevity.
3. Material Properties
- Breathability:
- Synthetic leather often lacks the natural breathability of genuine leather, which can make products uncomfortable for certain applications, such as footwear or seating.
- Flexibility vs. Strength:
- Balancing flexibility and durability is a challenge; overly flexible materials may be less durable, while stronger materials may feel rigid.
- Resistance to Wear:
- Ensuring resistance to UV rays, abrasion, and extreme temperatures can be technically challenging.
4. Cost Efficiency
- Raw Material Costs:
- High-quality polymers (e.g., advanced PU formulations) and additives can increase production costs.
- Energy-Intensive Processes:
- Processes like extrusion, coating, and curing require significant energy input, increasing operational costs.
- Competing with Genuine Leather:
- Balancing affordability while matching the premium appearance and feel of genuine leather can be difficult.
5. Technological Limitations
- Advanced Machinery:
- Manufacturing requires specialized machines for processes like coating, embossing, and curing, which are expensive to install and maintain.
- Process Complexity:
- Multi-step processes (e.g., coating layers, texturing, and finishing) require precise calibration, increasing the risk of production errors.
- Innovation:
- Developing new, sustainable materials (e.g., bio-based PU or plant-based leather) requires significant research and development investment.
6. Market and Consumer Perception
- Authenticity:
- Consumers may view synthetic leather as inferior to genuine leather in terms of quality and longevity.
- Ethical Concerns:
- Despite being animal-free, some consumers may still object to synthetic leather due to its reliance on petrochemicals and its environmental impact.
- Trends and Competition:
- Rapidly evolving fashion trends and competition from both genuine leather and alternative materials (e.g., mycelium leather) create market pressure.
7. Adhesion and Bonding Challenges
- Delamination:
- Ensuring strong adhesion between the polymer coating and the fabric backing is critical to avoid delamination over time.
- Compatibility:
- Selecting appropriate adhesives and primers for bonding synthetic leather layers is essential for durability.
8. Scalability
- Small Batch Production:
- Producing small batches of custom synthetic leather products can be less cost-effective than large-scale production.
- Customization Challenges:
- Meeting demands for specific colors, textures, and patterns while maintaining production efficiency is a logistical challenge.
9. Compliance with Regulations
- Chemical Restrictions:
- Compliance with environmental and safety regulations, such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in Europe, adds complexity.
- Fire Safety Standards:
- Synthetic leather used in furniture, automotive interiors, or aviation must meet stringent fire retardancy requirements.
10. Lifecycle Management
- Product End-of-Life:
- Developing recycling or upcycling methods for synthetic leather products is challenging due to their composite structure (plastic and fabric layers).
- Sustainability:
- Transitioning to sustainable alternatives, like bio-based or recyclable materials, requires innovation and capital investment.
11. Competition from Sustainable Alternatives
- Plant-Based Leathers:
- Materials like Piñatex (pineapple leather) and mycelium-based leather are gaining popularity, challenging synthetic leather manufacturers to innovate and differentiate.
- Genuine Leather:
- Genuine leather continues to appeal to premium markets, forcing synthetic leather manufacturers to match or exceed its quality while maintaining affordability.
12. Heat and UV Sensitivity
- Degradation:
- PVC and PU materials can degrade under prolonged exposure to sunlight and high temperatures, leading to discoloration, brittleness, or loss of integrity.
- Treatment Costs:
- Adding UV-resistant or heat-resistant coatings increases production costs.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Sustainable Innovation:
- Invest in bio-based or recyclable synthetic leather alternatives to address environmental concerns.
- Advanced Machinery:
- Adopt automated and precision-based manufacturing technologies to improve efficiency and quality control.
- Consumer Education:
- Highlight the benefits of synthetic leather, such as affordability, design versatility, and ethical considerations.
- Research and Development:
- Focus on improving material properties, such as breathability, durability, and appearance, to compete with genuine leather.
- Circular Economy Models:
- Develop take-back or recycling programs to minimize synthetic leather waste and enhance sustainability.
Conclusion
While synthetic leather offers many advantages, manufacturing it comes with challenges in environmental sustainability, quality control, and consumer perception. Overcoming these challenges requires innovation, efficient processes, and a focus on sustainability to meet the growing demands of a conscious consumer base.
Hashtags
#SyntheticLeatherChallenges #FauxLeatherProduction #ArtificialLeatherIssues #EcoFriendlyLeatherManufacturing #VeganLeatherHurdles #SustainableLeatherProblems #SyntheticMaterialProcessing #LeatherAlternativesManufacturing #FauxLeatherSustainability #ArtificialLeatherInnovationBarriers