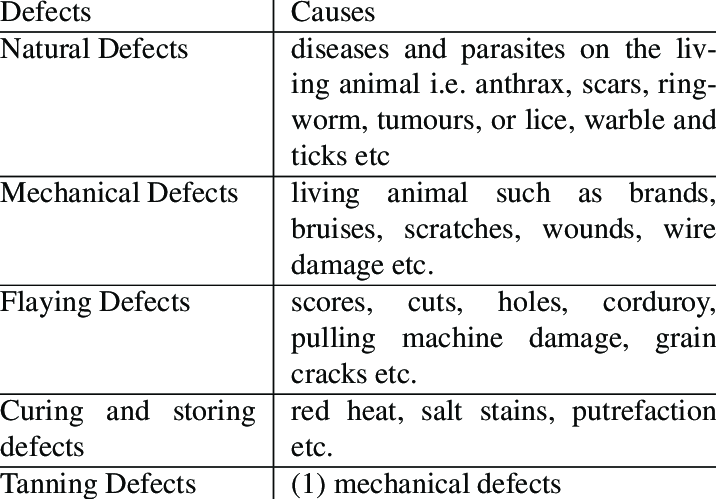
Leather accessories, though valued for their durability and style, can exhibit defects due to natural imperfections in the leather, manufacturing issues, or improper care. Here are the common defects found in leather accessories:
1. Natural Leather Defects
Leather, being a natural material, often has imperfections caused by the life of the animal.
Examples:
- Scars and Scratches:
- Visible marks caused by injuries or scratches on the animal’s skin.
- More common in full-grain leather.
- Insect Bites:
- Small holes or uneven textures from insect bites.
- Stretch Marks and Wrinkles:
- Natural creases or folds from the animal’s movements.
- Can affect the uniformity of the finished product.
- Veining:
- Visible veins on the surface, especially in thinner or lighter-colored leathers.
- Branding Marks:
- Marks from the animal being branded can appear on the hide.
2. Tanning and Finishing Defects
Defects may arise during the tanning or finishing processes that prepare the leather.
Examples:
- Color Inconsistency:
- Uneven dyeing or staining leading to blotchy or streaky finishes.
- Common in large accessories with expansive leather panels.
- Cracking or Dryness:
- Results from improper tanning or insufficient conditioning.
- Leads to a brittle, damaged surface over time.
- Loose Grain:
- A weak or flaky surface due to improper tanning.
- Appears as a peeling or “fuzzy” texture on the leather.
- Delamination:
- Separation of bonded leather layers, particularly in low-quality or synthetic leathers.
3. Manufacturing Defects
Errors during the cutting, stitching, or assembly process can lead to defects.
Examples:
- Uneven Stitching:
- Irregular or crooked stitches affecting aesthetics and durability.
- Loose threads or skipped stitches can compromise the product’s integrity.
- Misaligned Components:
- Handles, zippers, or pockets that are misaligned or unevenly attached.
- Rough Edges:
- Unfinished or poorly burnished edges, leading to fraying or uneven surfaces.
- Inadequate Bonding:
- Weak adhesive leading to parts separating (e.g., soles from leather uppers, pockets from bags).
- Hardware Issues:
- Faulty or poorly attached hardware (e.g., broken buckles, loose rivets, or misaligned zippers).
4. Usage and Wear Defects
Improper use, wear, or maintenance can result in defects over time.
Examples:
- Water Stains:
- Dark spots or discoloration caused by water exposure.
- Can lead to hardening or stiffening of the leather.
- Scratches and Scuffs:
- Surface damage from everyday use, particularly on smooth leather.
- Peeling or Flaking:
- Common in bonded or synthetic leather, where layers separate over time.
- Stretching or Deformation:
- Leather losing its shape due to overloading or improper storage.
- Fading or Discoloration:
- Caused by prolonged exposure to sunlight or harsh chemicals.
5. Defects in Synthetic Leather
Synthetic leather can exhibit specific defects due to its manufacturing process.
Examples:
- Cracking:
- Surface cracking due to low-quality materials or aging.
- Delamination:
- Layers of synthetic leather separating, often in low-cost items.
- Surface Bubbles:
- Uneven application of coatings causing air pockets or bubbles.
- Fading:
- Color loss from UV exposure or improper dyeing.
6. Environmental Damage
Exposure to extreme conditions can cause leather to deteriorate.
Examples:
- Mold and Mildew:
- Growth due to prolonged exposure to moisture or humidity.
- Appears as green or white spots and an unpleasant odor.
- Drying and Cracking:
- Happens when leather is stored in overly dry or hot conditions without conditioning.
- Salt Stains:
- White streaks caused by saltwater exposure or sweat.
7. Customization Errors
Mistakes during personalization or branding can result in aesthetic or functional defects.
Examples:
- Misaligned Embossing or Debossing:
- Logos, monograms, or patterns not properly centered or aligned.
- Overheated Stamps:
- Burn marks or discoloration from excessive heat during embossing.
- Poor Foil Stamping:
- Incomplete or peeling metallic foil used in custom designs.
8. Edge Defects
Poor finishing on leather edges can compromise the overall quality.
Examples:
- Fraying:
- Raw edges that fray over time, especially in untreated leather.
- Uneven Edge Paint:
- Paint on edges that chips, cracks, or appears inconsistent.
- Sharp Edges:
- Rough cuts that detract from the accessory’s comfort and appearance.
9. Hardware Issues
Hardware defects can impact both functionality and aesthetics.
Examples:
- Corrosion or Rust:
- Metal components like buckles, zippers, or rivets deteriorate due to moisture or poor-quality plating.
- Loose Attachments:
- Handles, straps, or decorative hardware that become detached.
- Malfunctioning Zippers:
- Zippers that stick, break, or fail to align properly.
10. Odor Issues
- Unpleasant Smells:
- Caused by poor tanning, storage in damp conditions, or chemical residues.
- Moldy Odor:
- Indicates moisture damage and potential mold growth.
Preventing Leather Defects
- Material Selection:
- Use high-quality leather and hardware to minimize natural and synthetic defects.
- Manufacturing Precision:
- Ensure accurate cutting, stitching, and finishing techniques.
- Proper Storage:
- Store leather accessories in dry, ventilated areas away from direct sunlight.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Clean, condition, and waterproof leather items to prevent wear and environmental damage.
- Quality Control:
- Implement thorough inspections at every production stage to catch defects early.
Conclusion
Common defects in leather accessories can result from natural imperfections, manufacturing errors, or improper care. Understanding these issues and implementing preventative measures during production and maintenance can ensure high-quality, long-lasting leather goods.
Hashtags
#LeatherAccessoryDefects #IdentifyingLeatherFlaws #QualityLeatherChecks #CommonLeatherIssues #LeatherCraftsmanshipChallenges #DefectiveLeatherGoods #LuxuryLeatherInspection #LeatherQualityControl #AvoidLeatherDefects #LeatherManufacturingHurdles