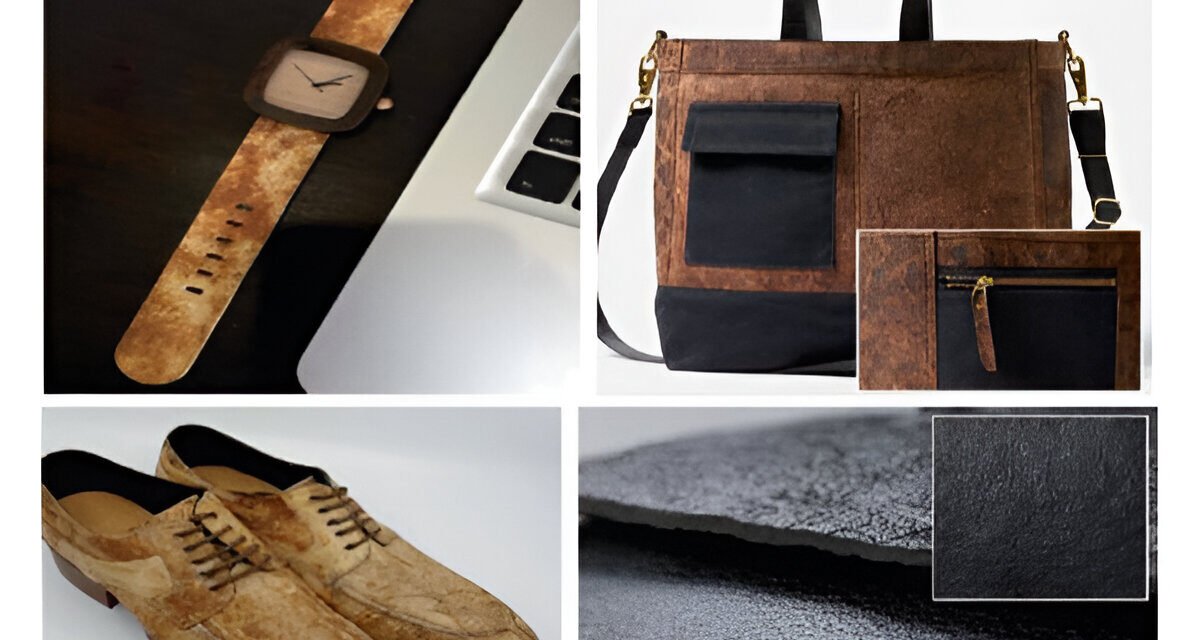
Bio-based synthetic leather is a rapidly growing field driven by the demand for sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives to traditional synthetic and genuine leather. These innovations aim to reduce environmental impact by using renewable, biodegradable, or recycled materials. Here are the key innovations in bio-based synthetic leather:
1. Plant-Based Materials
Bio-based synthetic leathers use natural fibers and plant-based polymers as their primary components.
Examples:
- Piñatex (Pineapple Leather):
- Made from cellulose fibers extracted from pineapple leaves (a byproduct of agriculture).
- Durable, lightweight, and versatile for fashion and upholstery.
- Cactus Leather:
- Derived from the prickly pear cactus.
- Requires minimal water to produce and is biodegradable.
- Known for its softness, durability, and UV resistance.
- Mushroom Leather (Mycelium):
- Made from the root structure of mushrooms, known as mycelium.
- Fast-growing and highly customizable in texture, thickness, and durability.
- Brands like Mylo™ by Bolt Threads are pioneering this innovation.
- Cork Leather:
- Made from the bark of cork oak trees.
- Naturally waterproof, lightweight, and sustainable due to its renewable harvesting process.
2. Bio-Polyurethane (Bio-PU)
Traditional PU synthetic leather relies on petroleum-based polymers. Bio-PU replaces a portion of the petroleum with plant-derived oils, such as:
- Soybean Oil.
- Castor Oil.
- Corn-Based Polymers.
Benefits:
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Maintains the flexibility and durability of traditional PU.
3. Recycled and Upcycled Materials
Bio-based synthetic leathers incorporate recycled fibers or repurposed agricultural and industrial byproducts.
Examples:
- Apple Leather:
- Made from apple peels and cores, a byproduct of the apple juice industry.
- Lightweight, soft, and suitable for fashion items like bags and shoes.
- Wine Leather (Vegea):
- Derived from grape skins, seeds, and stalks left over from wine production.
- Offers a luxurious finish similar to traditional leather.
- Banana Leather:
- Created from banana plant fibers, offering a natural texture and high durability.
4. Biodegradable Leather Alternatives
Bio-based synthetic leathers are designed to decompose naturally at the end of their lifecycle, reducing landfill waste.
Innovations:
- Mycelium-Based Leathers:
- Completely biodegradable under the right conditions.
- Algae-Based Polymers:
- Derived from algae, these polymers are both biodegradable and renewable.
- Chitosan-Based Leathers:
- Made from chitin (found in crustacean shells) blended with other plant materials, offering biodegradability and durability.
5. Advanced Fabric Backings
Many bio-based synthetic leathers use eco-friendly fabric backings made from:
- Recycled Polyester:
- Reduces plastic waste and extends the lifecycle of existing materials.
- Organic Cotton:
- Provides a natural, breathable base layer.
- Hemp and Jute:
- Renewable and durable options for backing layers.
6. Waterless and Solvent-Free Processes
Innovative production techniques are minimizing the environmental footprint of bio-based synthetic leather.
Examples:
- Waterless Dyeing:
- Uses eco-friendly dyes and requires little to no water.
- Solvent-Free Manufacturing:
- Eliminates harmful VOCs (volatile organic compounds) associated with traditional synthetic leather production.
7. Enhanced Performance Features
Bio-based synthetic leathers are engineered to match or exceed the performance of traditional leather in durability, flexibility, and aesthetics.
Features:
- Custom Textures:
- Innovations in embossing and coating allow for a wide range of finishes, from smooth to textured grains.
- Improved Durability:
- Bio-leathers are treated to withstand abrasion, water, and UV exposure.
- Lightweight Materials:
- Plant-based alternatives are often lighter than traditional leather, improving comfort and usability.
8. Circular Economy Models
Bio-based synthetic leather manufacturers are adopting circular economy principles by designing materials that can be reused or recycled.
Initiatives:
- Take-Back Programs:
- Brands collect used products to recycle or compost them.
- Closed-Loop Systems:
- Waste from production is reintroduced into the manufacturing process.
9. Consumer and Industry Adoption
- Fashion:
- Major brands like Stella McCartney, Adidas, and Hermès are incorporating bio-based synthetic leathers into their product lines.
- Automotive:
- Bio-leathers are being used in car interiors for eco-conscious consumers.
- Furniture and Upholstery:
- Designers are integrating plant-based leathers into sofas, chairs, and other furnishings.
10. Certifications and Transparency
Consumers are increasingly demanding proof of sustainability, leading to the development of certifications for bio-based synthetic leathers.
Common Certifications:
- Cradle to Cradle: Certifies products for environmental safety and circularity.
- Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS): Ensures organic content in textile backings.
- ECO PASSPORT by OEKO-TEX®: Verifies environmentally friendly materials and processes.
Challenges
Despite the progress, bio-based synthetic leathers face several challenges:
- Scalability:
- Producing bio-based alternatives at scale to meet global demand.
- Cost:
- Bio-based options are often more expensive than traditional synthetic leather due to complex manufacturing processes.
- Performance Gaps:
- Matching the durability and longevity of traditional synthetic and genuine leather.
- Consumer Awareness:
- Educating consumers about the benefits and proper care of bio-based materials.
Future Outlook
The bio-based synthetic leather industry is rapidly advancing, with ongoing research into new materials like seaweed, fungi, and agricultural byproducts. As production scales up and costs decrease, bio-based synthetic leather is poised to become a mainstream choice across industries, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Hashtags
#BioBasedSyntheticLeather #SustainableLeatherInnovation #EcoFriendlyFauxLeather #BioLeatherTechnologies #PlantBasedLeather #GreenLeatherAlternatives #VeganLeatherInnovation #SustainableMaterialTrends #BioLeatherRevolution #FutureOfSyntheticLeather