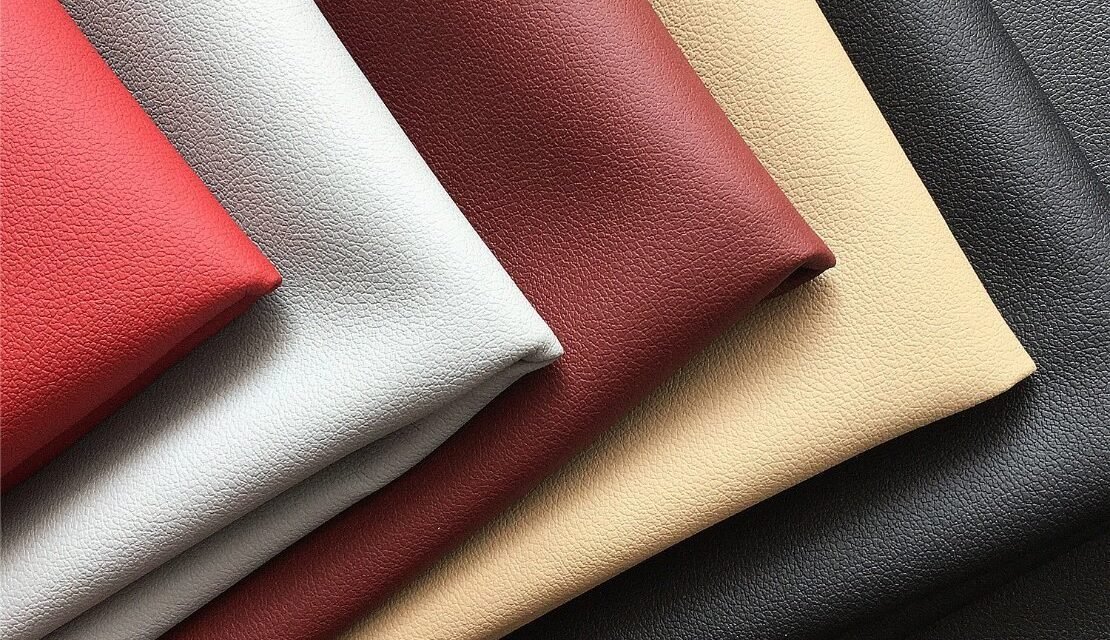
Synthetic leather, also known as faux leather, imitation leather, or vegan leather, is made from a combination of plastic polymers and other materials designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather. Here’s an overview of its composition and the materials commonly used:
1. Plastic Polymers
Synthetic leather typically uses one or more plastic polymers as its primary material. These polymers form the durable and flexible base layer.
a. Polyurethane (PU) Leather
- Composition:
- Made by coating a fabric base (e.g., polyester or cotton) with a polyurethane layer.
- Features:
- Softer and more flexible than PVC leather.
- Breathable and more environmentally friendly compared to PVC.
- Applications:
- Widely used in furniture, clothing, and fashion accessories.
b. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather
- Composition:
- Made by applying a PVC coating over a fabric backing.
- Features:
- Durable, water-resistant, and affordable.
- Less flexible and breathable than PU leather.
- Applications:
- Often used for upholstery, automotive interiors, and inexpensive footwear.
2. Fabric Base Layer
- Materials:
- Polyester, cotton, or a blend of synthetic and natural fibers serves as the base or backing material.
- Purpose:
- Provides structure, strength, and flexibility to the synthetic leather.
- Variations:
- High-quality synthetic leather may use dense, woven fabrics for enhanced durability and comfort.
3. Additives and Plasticizers
- Plasticizers:
- Added to PVC or PU to increase flexibility and make the material softer and more leather-like.
- Stabilizers:
- Protect the material from degradation caused by UV rays or heat.
- Colorants:
- Pigments or dyes are used to achieve various colors and finishes.
- Texturing Agents:
- Create grain patterns to mimic the look of natural leather.
4. Surface Coating
- Polymer Layers:
- Additional layers of polyurethane or other coatings are applied to create the desired finish and texture.
- Embossing:
- Grain patterns are embossed onto the surface to replicate the appearance of genuine leather.
- Gloss or Matte Finish:
- The final coating determines the sheen, ranging from high gloss to a matte look.
5. Alternatives in Sustainable Faux Leather
With the rise of eco-conscious consumer demand, new forms of synthetic leather are being developed that incorporate more sustainable materials:
a. Bio-Based PU Leather
- Composition:
- Uses bio-based polyurethane derived from renewable sources like soybeans, corn, or castor oil.
- Features:
- Lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based PU.
b. Plant-Based Leather
- Composition:
- Made using organic materials like pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, cork, or mushrooms (mycelium).
- Features:
- Eco-friendly, biodegradable, and cruelty-free.
Comparison to Genuine Leather
| Feature | Synthetic Leather | Genuine Leather |
| Material | Plastics (PU, PVC, etc.) | Animal hide |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to cracking | Long-lasting with proper care |
| Breathability | Limited | Natural and breathable |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | More expensive |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-based, some eco-friendly options | Biodegradable but involves ethical concerns |
Conclusion
Synthetic leather is primarily made of plastic polymers (PU or PVC) combined with fabric backing and surface coatings to mimic the look and feel of natural leather. With advancements in technology, plant-based and bio-based alternatives are increasingly being developed to address environmental concerns and provide more sustainable options.
Hashtags
#SyntheticLeatherMaterials #WhatIsSyntheticLeather #FauxLeatherFacts #EcoFriendlyLeather #PUAndPVCLeather #LeatherAlternatives #VeganLeatherInfo #ArtificialLeatherComponents #SustainableLeatherOptions #SyntheticLeatherProduction